
Animal Cell Definition Structure Parts Functions Labeled Diagram Riset
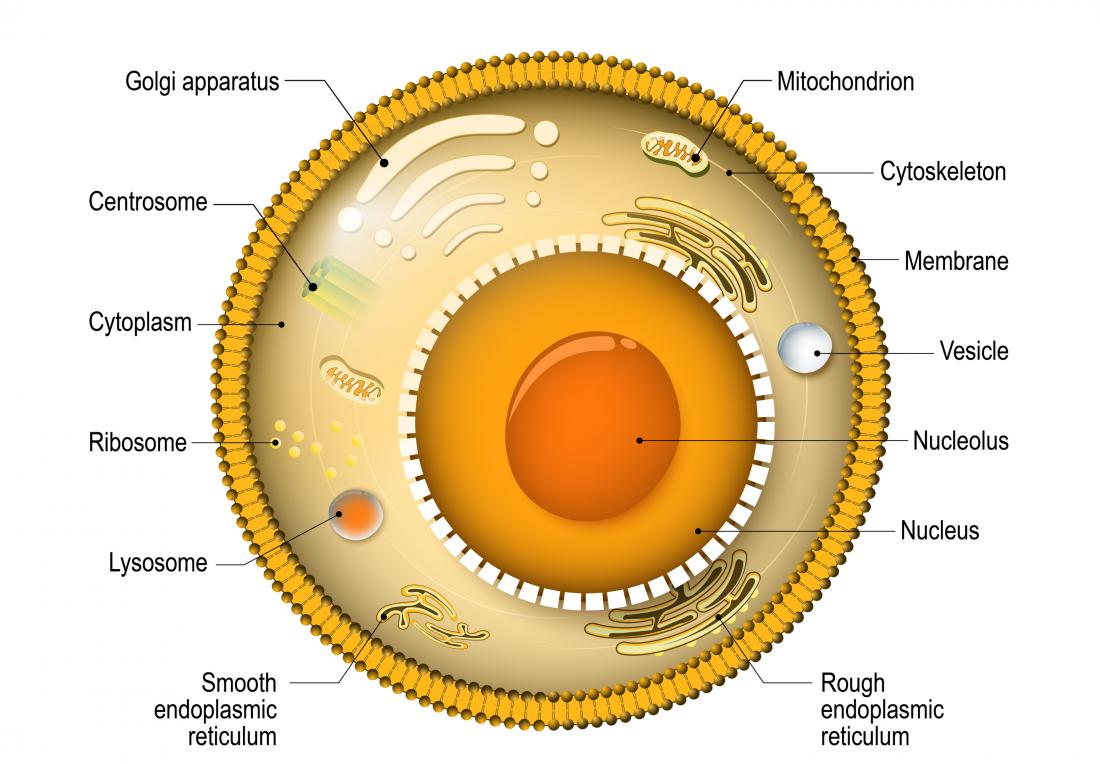
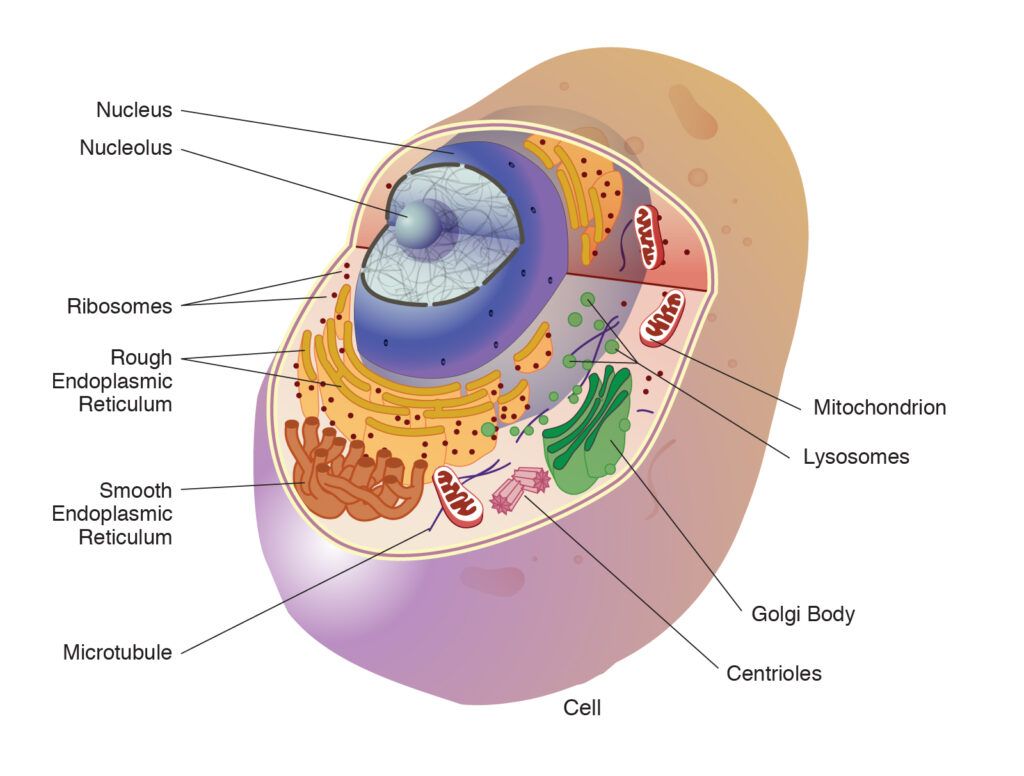
An organelle is a structure within the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell that is enclosed within a membrane and performs a specific job. Organelles are involved in many vital cell functions. Organelles in animal cells include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, and vacuoles. Ribosomes are not enclosed within a membrane, but they are still commonly referred.
The cell Types, functions, and organelles
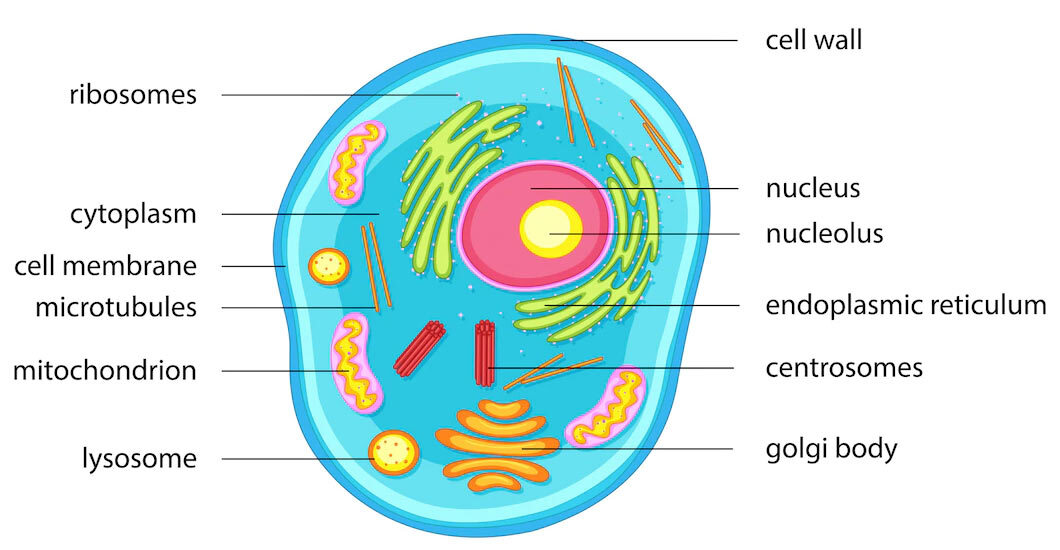
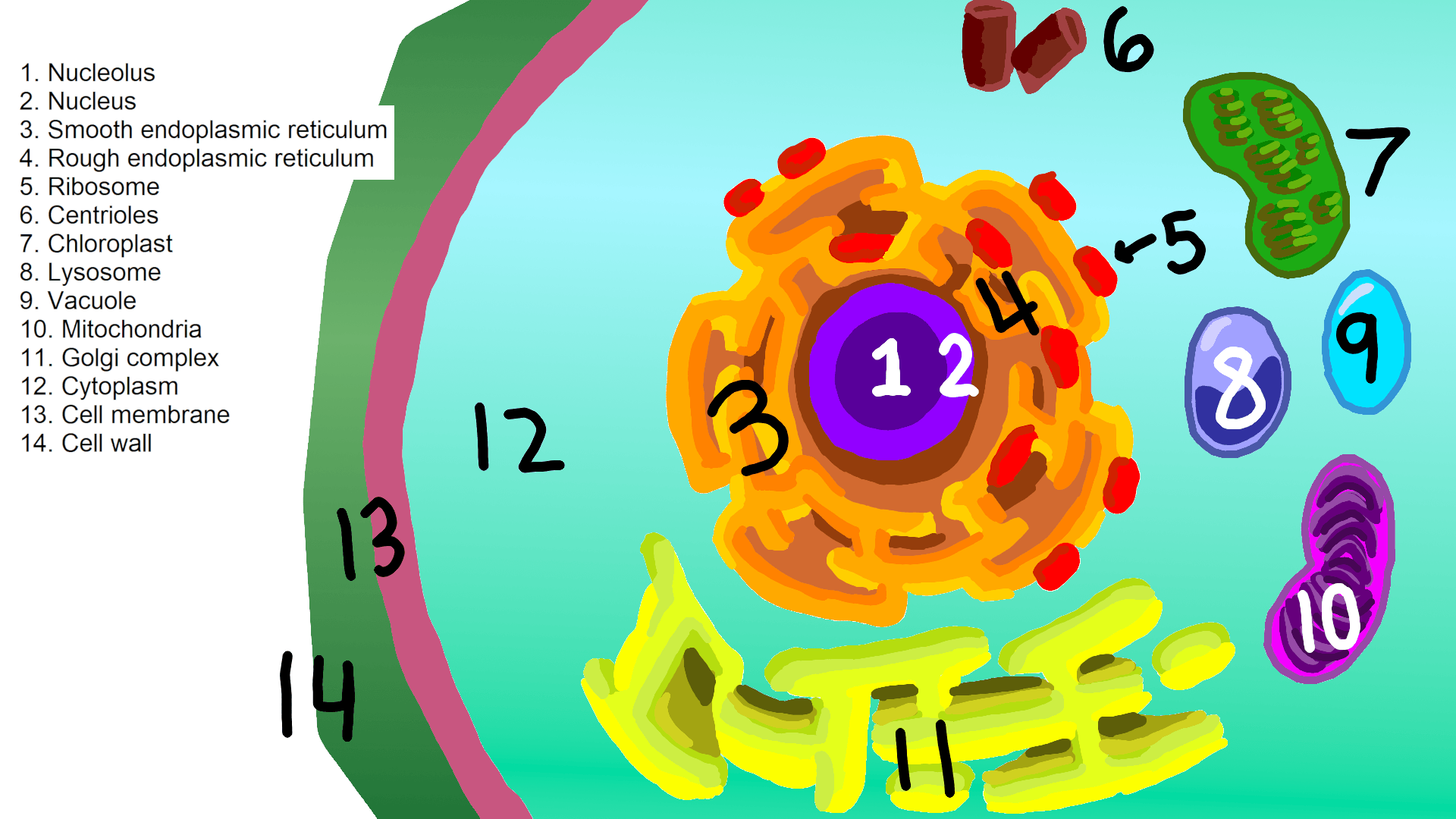
Distinguishing characteristics of a plant cell are its cell wall, chloroplasts, and large vacuole. A plant cell is the basic building block of a plant. Plant cells, like all eukaryotic cells, contain a nucleus and other organelles, each with its distinct functions. However, plant cells also possess unique components that differentiate them from.

Chapter 3 Cell Structure and Control Diagram Quizlet
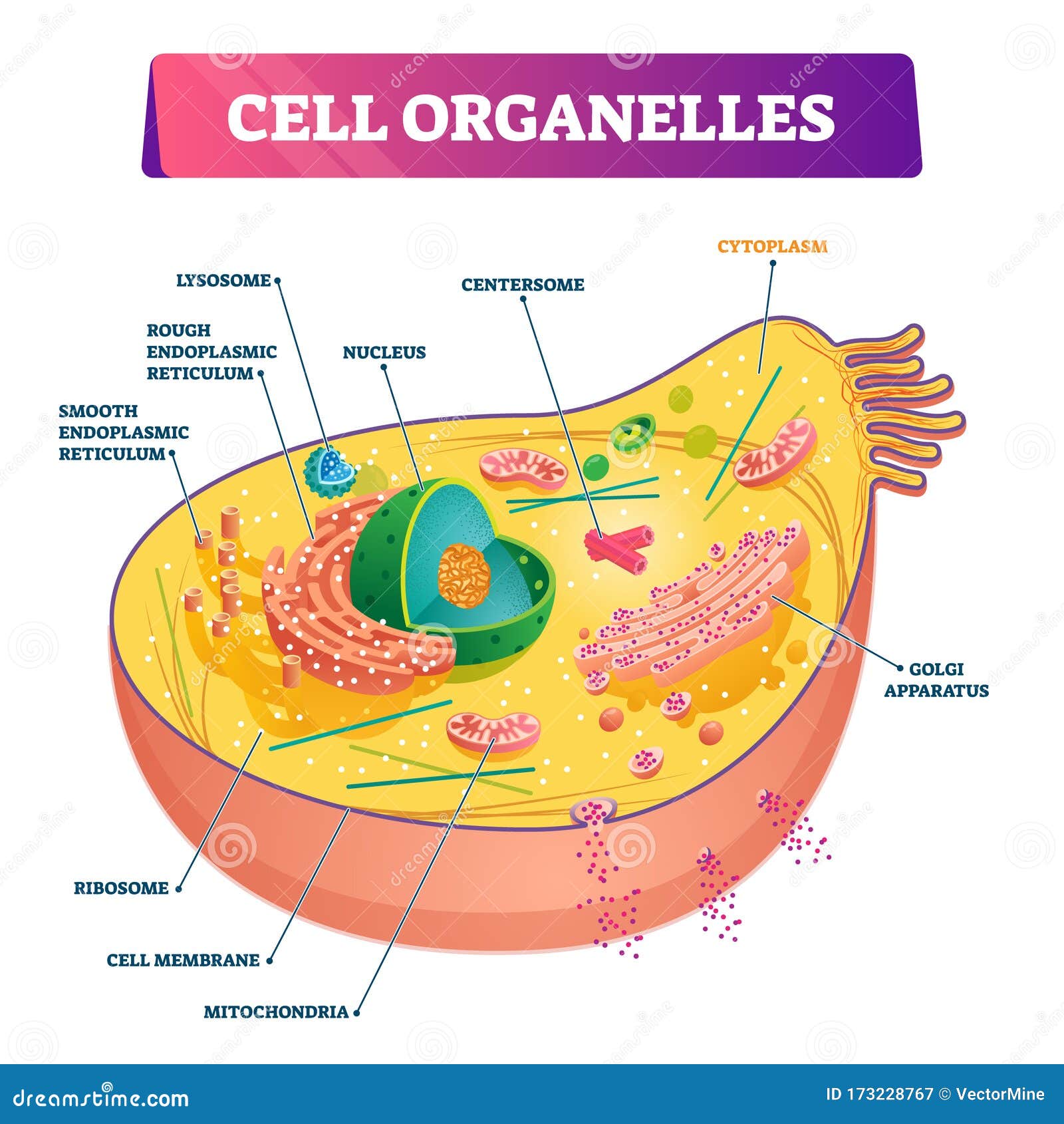
Cell Organelles Types (With Diagram) Article Shared by. ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the ten main types of cell organelles present in the cell. The types are: 1. Nucleus 2. Plastids 3. Mitochondria 4. Endoplasmic Reticulum 5.
Cell Organelle
numerous membrane-bound organelles—such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; several, rod-shaped chromosomes;. In Figure 8b, the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell.

Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Structure, Eukaryotic Cells INFOhio Open Space
Cell size. Typical prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in diameter and are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which usually have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm. The figure below shows the sizes of prokaryotic, bacterial, and eukaryotic, plant and animal, cells as well as other molecules and organisms on a.
The Cell Organelles Concise Medical Knowledge
Figure 5.6.1 5.6. 1: Ribosomal subunit. An organelle is a structure within the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell that is enclosed within a membrane and performs a specific job. Organelles are involved in many vital cell functions. Organelles in animal cells include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, and.

cell Definition, Types, Functions, Diagram, Division, Theory, & Facts
Therefore, not every animal cell has all types of organelles, but in general, animal cells do contain most (if not all) of the following organelles. Additionally, some organelles will be highly abundant in certain cells and not others. Labeled diagram of a typical animal cell Nucleus. The nucleus contains all the genetic material in a cell.

Schematic illustration to show the 22 organelles or subcellular
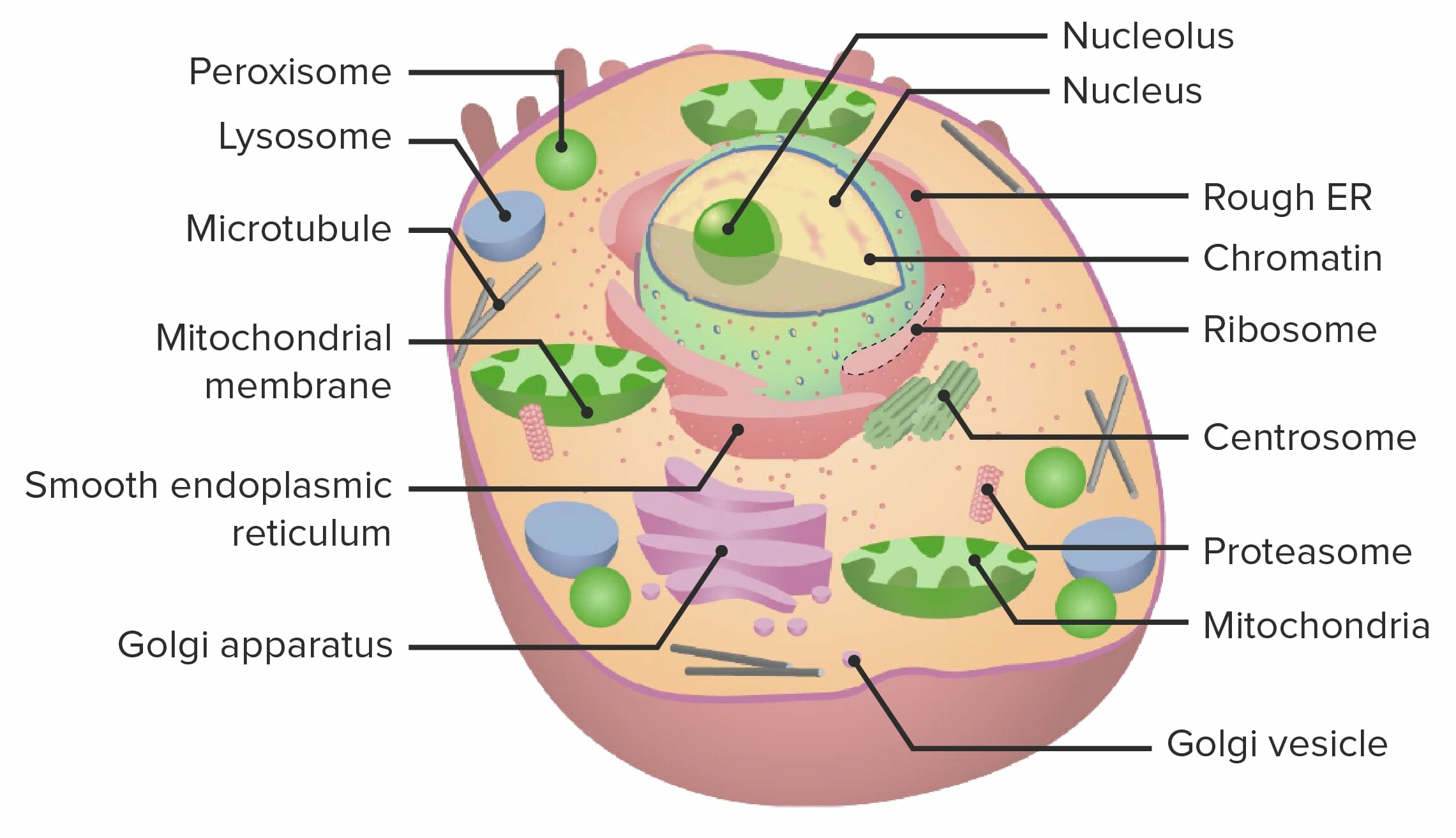
Organelle. In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name organelle comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence organelle, the suffix -elle being a diminutive. Organelles are either separately enclosed within their own lipid.

Cell Organelles Structure and their Functions
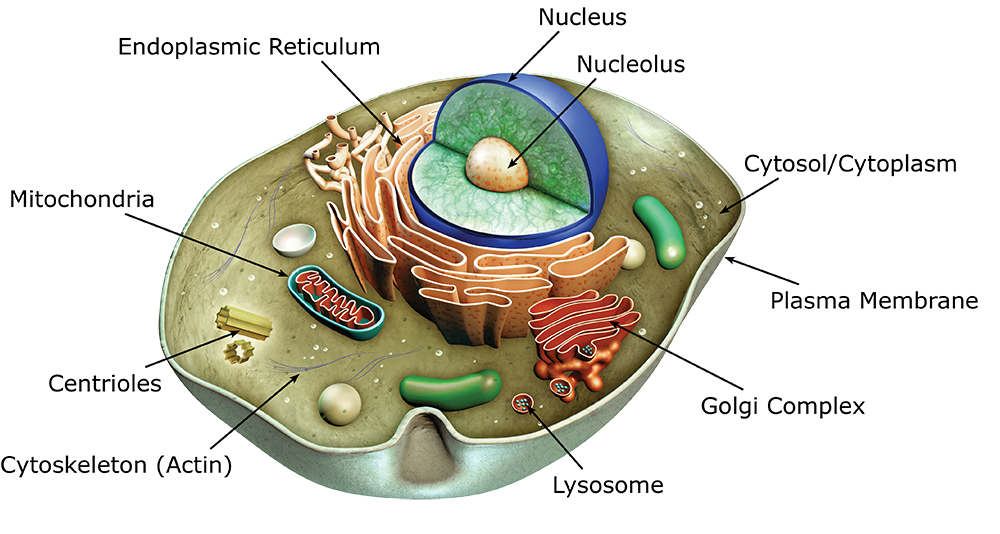
A diagram representing the cell as a factory. The cell membrane is represented as the "factory walls." The nucleus of a cell is represented as the "blueprint room.". An organelle (think of it as a cell's internal organ) is a membrane bound structure found within a cell. Just like cells have membranes to hold everything in, these mini.

Cell Organelles Structure Cell Organelles
It is made up of several types of organelles that allow the cell to function and reproduce. There are two general classes of cells that exist: the self-sustaining simple cells known as prokaryotic (bacteria and archaea) and the more complex dependent cells known as eukaryotic. The eukaryotic cells types are generally found in animals, plants.
Cell Organelles Definition, Structure, Types, Functions
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells, meaning they possess a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have cell walls, allowing for more flexibility in shape and movement. A plasma membrane encloses the cell contents of both plant and animal cells, but it is the outer coating of an animal cell.

301 Moved Permanently
Key points: All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. The cell membrane surrounds a cell's cytoplasm, which is a jelly-like substance containing the cell's parts. Cells contain parts called organelles. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Eukaryotic_Cell_animal-59df7d9f03f40200104fcd0b-5c2e86f7c9e77c00019f8855.jpg)
Animal Cells and the MembraneBound Nucleus
Diagram of Microtubules Functions of Microtubules. Transportation of some organelles like the mitochondria and the vesicles i.e. transporting vesicles from the neuron cell body to the axon tips, and back to the cell body; Structural support, they give characteristic support to the Golgi bodies, holding them within the gel-matrix of the cytoplasm.
All about Human Cells Universal Health Products
Cell organelles are specialized entities present inside a particular type of cell that performs a specific function. There are various cell organelles, out of which, some are common in most types of cells like cell membranes, nucleus, and cytoplasm. However, some organelles are specific to one particular type of cell-like plastids and cell.
Cell Structures and Organelles AAT Bioquest
Organelles are small structures within the cytoplasm that carry out functions necessary to maintain homeostasis in the cell. They are involved in many processes, for example energy production, building proteins and secretions, destroying toxins, and responding to external signals. Organelles are considered either membranous or non-membranous.
Cell Organelle — Types & Functions Expii
cell, in biology, the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. These cells cooperate with other specialized cells and become.